VIDAS® C. difficile panel
Schnelle Identifizierung von C. difficile Infektionen
Das VIDAS® C. difficile Panel enthält zwei komplementäre Tests zur Hilfestellung bei der Diagnostik von C. difficile Infektionen.
- Automatisierte und benutzerfreundliche Tests für schnelle Ergebnisse
- Vereinfacht die Diagnostik
- Flexible Lösung für kleine oder große Testvolumina
- Ausschluss negativer Patienten in nur 50 Minuten (VIDAS® GDH)
Benötigen Sie weitere Informationen?
VIDAS® C. difficile GDH ist ein qualitativer Test zum Nachweis des C. difficile Antigens Glutamat-Dehydrogenase (GDH) in Stuhlproben von Patienten mit Verdacht auf eine C. difficile Infektion. Zusammen mit dem VIDAS® C. difficile Toxin A & B wird dieser Test im Rahmen eines zweistufigen Algorithmus verwendet. Beide Tests basieren auf der ELFA (Enzyme-Linked-Fluorescent-Assay) Technik.
Das VIDAS® C. difficile Panel liefert Ihnen schnell die Informationen, die Sie brauchen, um die Infektion nachzuweisen und deren Ausbreitung zu verhindern¹. Dadurch werden die Morbiditäts- und Mortalitätsraten gesenkt und menschliche sowie wirtschaftliche Belastungen durch C. difficile in Krankenhäusern und Gesundheitseinrichtungen reduziert.
Teststrategien
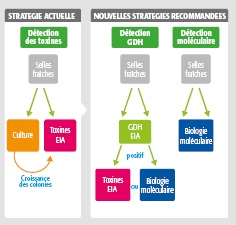
Gemäß den neuen Leitlinien*, sollten positive GDH Ergebnisse auf C. difficile Toxin A & B getestet werden, um eine C. difficile Infektion zu bestätigen.
* Siehe Reiter INFORMATIONSPORTAL
Zuverlässigkeit
Das VIDAS® C. difficile Angebot hilft Ihnen, das Patientenmanagement zu verbessern:
- VIDAS® C. difficile GDH: verfügt über einen hohen negativen Vorhersagewert (Negative Predictive Value, NPV)*, für den sicheren Ausschluss von C. difficile Infektionen
|
VIDAS® GDH VERSUS CCFA**
(306 POSITIFS ET 1598 NÉGATIFS)
|
VIDAS® GDH VERSUS CHROMID® C. DIFFICILE
(350 POSITIFS ET 1554 NÉGATIFS)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| NPV | 99.1% [98.5 – 99.5]% | 98.3% [97.5 – 98.9]% |
| Sensitivität | 95.8% [92.8 – 97.7]% | 92.9% [89.6 – 95.3]% |
| Spezifität | 90.0% [88.4 – 91.4]% | 91.8% [90.3 – 93.1]% |
- VIDAS® C. difficile Toxin A & B: hohe Spezifität* vermeidet unnötige Mehrfachtestungen
Die Vorteile dieser LösungNACH OBEN
- Automatisiert und benutzerfreundlich: die Familie der VIDAS® Immunoanalyzer wird auf Grund ihrer Flexibilität, Benutzerfreundlichkeit und problemlosen Einbindung in den Arbeitsablauf des Labors weltweit geschätzt
- Schnelle Ergebnisse: nur 50 Minuten für VIDAS® C. difficile GDH und 75 Minuten für VIDAS® C. difficile Toxin A & B
- Entspricht den neuen Richtlinien*
- Kosteneffizient:
- Vermeidet unnötige Tests zur besseren Kostenkontrolle
- Abarbeitung von Einzelproben, bedarfsgerecht für hohes oder niedriges Testaufkommen bei lokalen oder epidemischen Ausbrüchen
- Hinweise auf epidemiologische Trends: durch die Aufzeichnung der getesteten Proben und deren Ergebnisse
* Siehe Reiter INFORMATIONSPORTAL
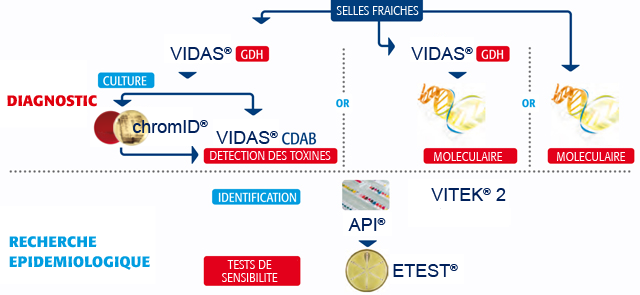
bioMérieux’s C. difficile Gesamtangebot
bioMérieux bietet die erste auf dem Markt erhältliche C. difficile Gesamtlösung:
|
Methode |
Produktname |
Referenz-Nummer |
|---|---|---|
|
Screening |
VIDAS® GDH |
Ref. 30125 |
|
Toxin Nachweis |
VIDAS® C. difficile Toxin A&B |
Ref. 30118 |
|
Kulture |
chromID® C. difficile agar |
Ref. 43871 |
|
Identifizierung |
VITEK® 2 ANC card |
Ref. 21347 |
|
Empfindlichkeitsprüfung |
ATB™ ANA2 |
Ref. 142691 |
|
Überwachung |
VIGIguard™ |
References
(2) Siegel JD, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, Chiarello L, and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, 2007 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings.
| VIDAS® C. difficile GDH |
VIDAS® C. difficile Toxin A & B |
|
|---|---|---|
| Referenznummer | 30125 | 30118 |
| Tests/Packung | 60 | 60 |
| Testzeit | 50 Minuten | 75 Minuten |
| Probenart | Stuhlprobe | Stuhlprobe |
| Stuhlprobe - Volumen Probenvolumen nach Vorbehandlung |
200 µL 300 µL |
200 µL 300 µL |
| Kalibrationsintervall | 28 Tage | 14 Tage |
Related Publications
ECCMID 2014
J. Van Broeck, E. Ngyuvula Mantu, K. Soumillion, M. Delmée . Evaluation of the impact of freezing on positive Clostridium difficile stools using VIDAS® GDH & VIDAS® CD toxins A/B, Liaison GDH, Liaison toxins A&B and C. DIF QUIK CHEK Complete®.
ECCMID 2013 Abstract R2753
L. De Cooman, S. Drieghe, I. Leroux-Roels, G.Glaeys. J. Boelens. Evaluation of the VIDAS® Gultamase Dehydrogenase Test (bioMérieux) for algorithm-based Clostridium difficile testing.
ECCMID 2013 Poster P187
C.Eckert, O. Said, C. Rambaud, N. Poccardi, B. Burghoffer, V. Lalande, F. Barbut. Comparison of the VIDAS® C. difficile GDH and the GDH component of the C. diff Quik Chek Complete for detection of Clostridium difficile in stools.
ECCMID 2013 Poster 1872
D. Achleiter, A. Wutscher, M. Hell. Evaluation of the new VIDAS GDH (ELFA) Test and VIDAS Clostridium difficile Toxin A&B Test compared to a 3-Step Toxin B-PCR based-algorithm at a University Hospital.
ECCMID 2012 P2266
Davies, K. A., Bosomworth, C. E., Carricajo, A., Adam, T. and Wilcox, M.H. Comparison of VIDAS® GDH automated immunoassay with Cepheid GeneXpert® C. difficile PCR assay and an in-house PCR assay for GluD, for the detection of C. difficile in faecal samples.
Guidelines
New C. difficile testing algorithm guidelines recommend the use of a two-step protocol starting with a GDH enzyme immunoassay (EIA) followed by a sensitive toxin EIA to confirm positive results. A culture test then establishes sensitivity for results similar to the “gold standard” culture + toxin test.


Die Bedeutung einer schnellen C. difficile Diagnostik
Ein Blick auf die Fakten macht schnell klar, warum eine schnelle C. difficile Diagnostik so wichtig ist:
- Clostridium difficile verursacht ca. 15-25 % der Antibiotika assoziierten Diarrhoen1
- Prävalenz: 13,1 / 1.000 Patienten in den USA²
- Zunehmende Inzidenz: In Sachsen (Deutschland) stieg die Infektionsrate von 1,7 bis 3,8 Fälle pro 100.000 Einwohner im Jahr 2002 auf 14,8 Fälle pro 100.000 Einwohner im Jahr 2006³ an und liegt damit höher als die Inzidenz von MRSA
- Ältere und immungeschwächte Patienten sind besonders gefährdet sich mit C. difficile zu infizieren und ernsthaft und schwer zu erkranken1
- Hochansteckende Stämme breiten sich zunehmend aus1
- Schwere Ausbrüche, erhöhte Morbidität und Mortalität nehmen dramatisch zu (Mortalität (USA): 6-15%)4
- Wirtschaftliche Belastung: 3,2 Mill. $ in den USA und 3 Milliarden Euro in Europa5
1. Bartlett JG. Clinical practice. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med 2002;346:334-349
http://www.cdc.gov/HAI/organisms/cdiff/Cdiff_faqs_HCP.html#a1
2. Jarvis WR. et al.: National point prevalence of Clostridium difficile in US health care facility inpatients. AJIC 2009 37:263-270
3. Rupnik M. et al.: Clostridium difficile infection: new developments in epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nature reviews microbiology. 2009;7:10.1038/nrmicro2164.
4. Bartlett JG. et al. Clinical recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:S12-18.
5. Barbut F. et al. A European survey of diagnostic methods and testing protocols for Clostridium difficile. ESCMID study group report. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:989-996